Install and Operation
ModelBox can be installed and run in several models depending on the use case. Here we review a few of those use cases and discuss possible ways to run and operate the service.
Service Components
The service consists of the following components -
- ModelBox Server - The central control plane of ModelBox stores metadata related to experiments and models.
- Metadata Storage Backend - Storage service for experiment and model metadata.
- Blob Server - The server can be optionally run in the blob serving mode, where it only offers APIs to download and upload artifacts.
- Metrics Backend - Storage service for time series data of experiments and models.
Evaluating ModelBox Locally
The best way to evaluate ModelBox is to run it locally using ephemeral storage. This mode allows users to train new models and learn how to log, read and compare metadata using the SDK without thinking about deploying in a cluster.
Configuration
Generate the default config for ModelBox server. The CLI has a command to generate the default config. It generates configuration to run the server with ephemeral storage.
$ modelbox server init-config
The config generated should be the following in a file called modelbox_server.toml -
artifact_storage = "filesystem"
metadata_storage = "ephemeral"
metrics_storage = "inmemory"
listen_addr = ":8085"
[artifact_storage_filesystem]
base_dir = "/tmp/modelboxblobs"
[artifact_storage_s3]
region = "us-east-1"
bucket = "modelbox-artifacts"
[metadata_storage_integrated]
path = "/tmp/modelbox.dat"
[metadata_storage_postgres]
host = "172.17.0.3"
port = 5432
username = "postgres"
password = "foo"
dbname = "modelbox"
[metadata_storage_mysql]
host = "172.17.0.2"
port = 3306
username = "root"
password = "foo"
dbname = "modelbox"
[metrics_storage_timescaledb]
host = "172.17.0.4"
port = 5432
username = "postgres"
password = "foo"
dbname = "modelbox_metrics"
Start the Server
$ modelbox server start --config-path ./path/to/modelbox_server.toml
That's it! Once the server is started, the ModelBox SDK or CLI can be used to interact with the service.
Thoughts on Production Deployment Scenarios
In production, it is expected that HA data storage services are used for metadata and metrics storage. The ModelBox server should also run in a HA mode by running multiple instances of the server in a cluster. The service metrics should be monitored, and the appropriate number of instances of services should be chosen to keep the API latency and resource usage of the server to reasonable limits.
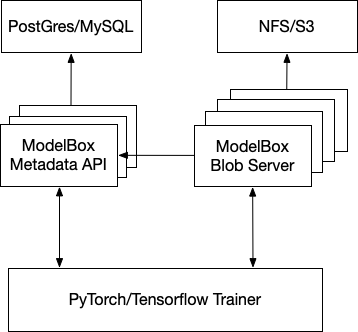
ModelBox supports the following databases, metrics and blob storage services -
Metadata Store
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- Ephemeral Storage
Metrics Store
- Timescaledb
- Ephemeral Storage
Artifacts and Blob Storage
- AWS S3
- File System(Ephemeral, NFS)
Build ModelBox
ModelBox can be built from source or be downloaded from GitHub.
Building from Source using GoReleaser
Install goreleaser from here. After it’s installed, the binary can be built.
goreleaser build --rm-dist --snapshot